A healthy smile is more than just an aesthetic goal; it’s a crucial part of your overall well-being. However, one of the most common oral health challenges many people face is tartar buildup. Also known as calculus, tartar can lead to gum disease, cavities, and other dental problems if not addressed.
With the growing popularity of water flossers, many wonder if these handy devices can remove tartar. Short answer? Not exactly—but they’re still an important part of your oral care arsenal. Read on to learn everything about tartar, water flossers, and how you can maintain a pristine smile.

What Is Tartar and Why Is It a Problem?
Tartar is a hardened form of dental plaque that clings stubbornly to your teeth and gumline. It develops when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, combines with food particles and minerals in your saliva. If you don’t remove plaque promptly through proper brushing and flossing, it calcifies into tartar.
Why is this a big deal? Tartar isn’t just unsightly; it can wreak havoc on your oral health. Beyond the yellowish or brownish look it gives your teeth, tartar creates a rough surface that attracts more plaque and bacteria. This can irritate your gums, leading to gum disease, bad breath, and even tooth loss in severe cases.
The tough nature of tartar means you can’t brush or floss it away once it forms. Removing it requires the tools and expertise of a professional dentist.
The Science Behind Tartar Formation
Understanding how tartar forms helps illustrate why prevention is so critical. The process starts with plaque, which is made up of bacteria constantly forming on your teeth. The bacteria feed on sugars and starches from food, producing acids that can harm enamel and irritate gums.
If plaque isn’t removed within 24–72 hours, it hardens into tartar due to the presence of minerals in your saliva. Once tartar forms, it adheres tightly to your teeth and gumline, making it impossible to remove with at-home tools.
Tartar can form in hard-to-reach areas, like the back of your teeth or between them, which emphasizes the importance of thorough oral hygiene.
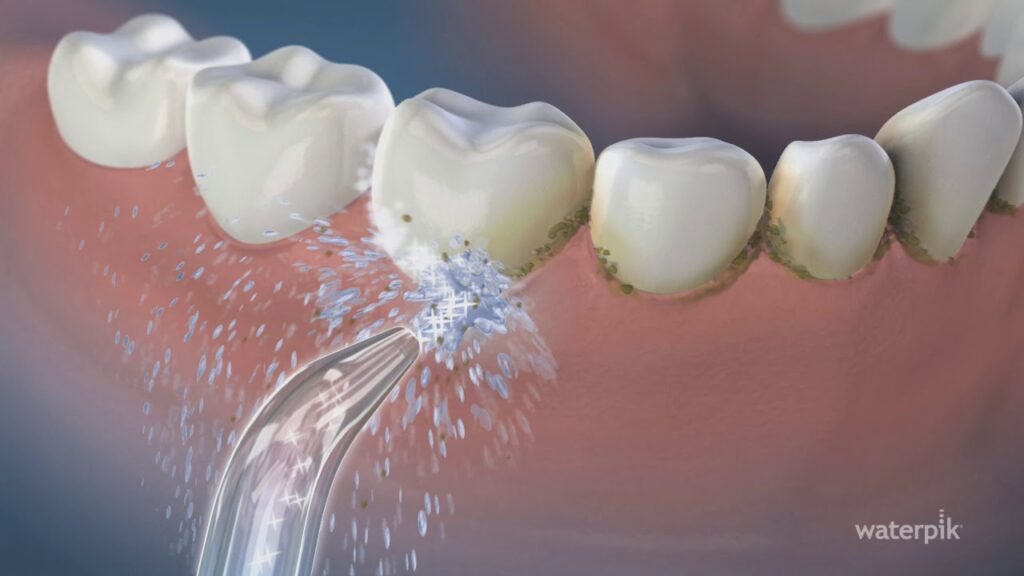
Do Water Flossers Remove Tartar?
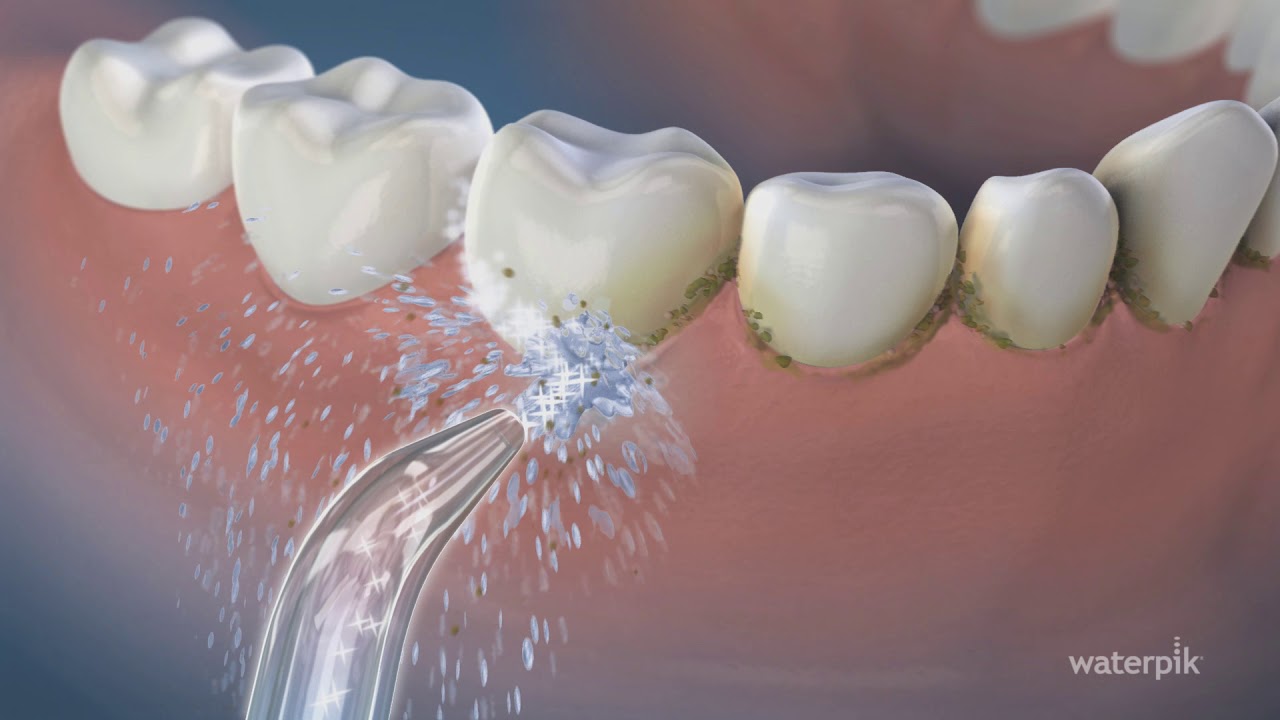
Water flossers, like the popular Waterpik, are often marketed as a user-friendly alternative to traditional flossing. They use a pressurized stream of water to clean between your teeth and along your gumline. While water flossers are effective at dislodging food particles and softening plaque, they cannot remove tartar.
Tartar is essentially hardened plaque that’s bonded to your tooth surface. No matter how strong the water stream, once plaque becomes tartar, it’s there to stay until removed professionally.
Here’s the good news: Water flossers can help prevent tartar by reducing the plaque that leads to it. When used consistently and correctly, they can be an excellent addition to your daily oral care routine.
The Unique Benefits of Water Flossers
While they can’t eliminate tartar, water flossers offer plenty of benefits that make them worth including in your routine. Here’s how they stand out:
1. Gentle on Sensitive Teeth and Gums
If you have sensitive teeth, receding gums, or existing gum disease, traditional flossing may feel uncomfortable. Water flossers provide a gentler way to clean without causing irritation.
2. Effective for Braces and Dental Work
Traditional flossing can be a challenge if you have braces, bridges, or dental implants. Water flossers make it easier to clean around brackets, wires, and other tricky areas, helping you maintain good hygiene.
3. Prevents Plaque Accumulation
By rinsing away food particles and soft plaque, water flossers reduce the risk of plaque hardening into tartar. They’re particularly helpful for cleaning along the gumline, where plaque often starts to accumulate.
4. Improves Gum Health
Some studies show that water flossers are as effective as traditional floss in reducing gum inflammation and bleeding. The pulsing water stream can massage the gums, improving blood circulation and overall gum health.

How to Use a Water Flosser for Best Results
To get the most out of your water flosser, follow these simple steps:
- Fill the Reservoir
Add lukewarm water to the device’s reservoir. For added benefits, you can mix in a mouthwash approved by your dentist. - Adjust the Pressure
Start on a low setting and gradually increase the pressure as you get used to the feeling. If you have sensitive gums, stick with gentle pressure. - Aim Carefully
Lean over the sink to avoid splashing, hold the flosser perpendicular to your gumline, and trace each tooth. Spend extra time on hard-to-reach areas. - Clean Consistently
Use your water flosser once a day, preferably before bedtime, to remove debris from the day.
Remember, while water flossers are a handy tool, they should complement—not replace—brushing and traditional flossing.
Preventing Tartar Formation at Home
The best way to combat tartar is to stop it in its tracks. Here’s your game plan for keeping your teeth and gums healthy and tartar-free:
- Brush Thoroughly
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush at least twice a day for two minutes, focusing on all tooth surfaces and the gumline. - Floss Regularly
Whether you choose string floss, picks, or a water flosser, cleaning between your teeth removes plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach. - Rinse Effectively
Use an antiseptic or fluoride mouthwash to help eliminate bacteria and strengthen enamel. - Mind Your Diet
Reduce sugary and starchy foods that feed bacteria. Include crunchy fruits and veggies like apples and carrots, which can help scrub plaque naturally. - Don’t Skip Dental Appointments
Regular professional cleanings are crucial for removing tartar and spotting dental issues early.
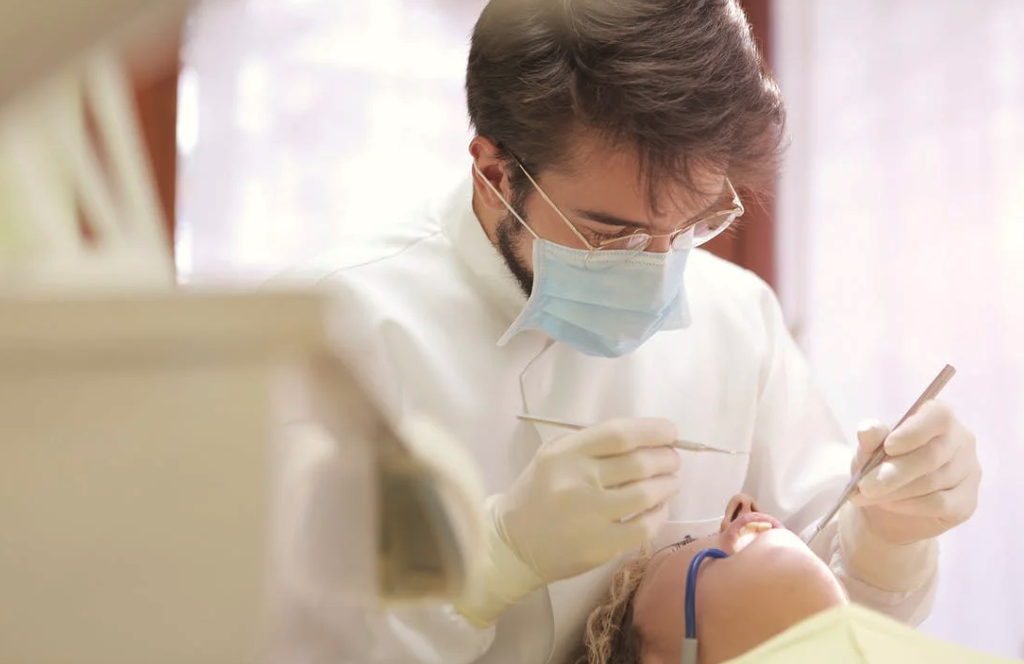
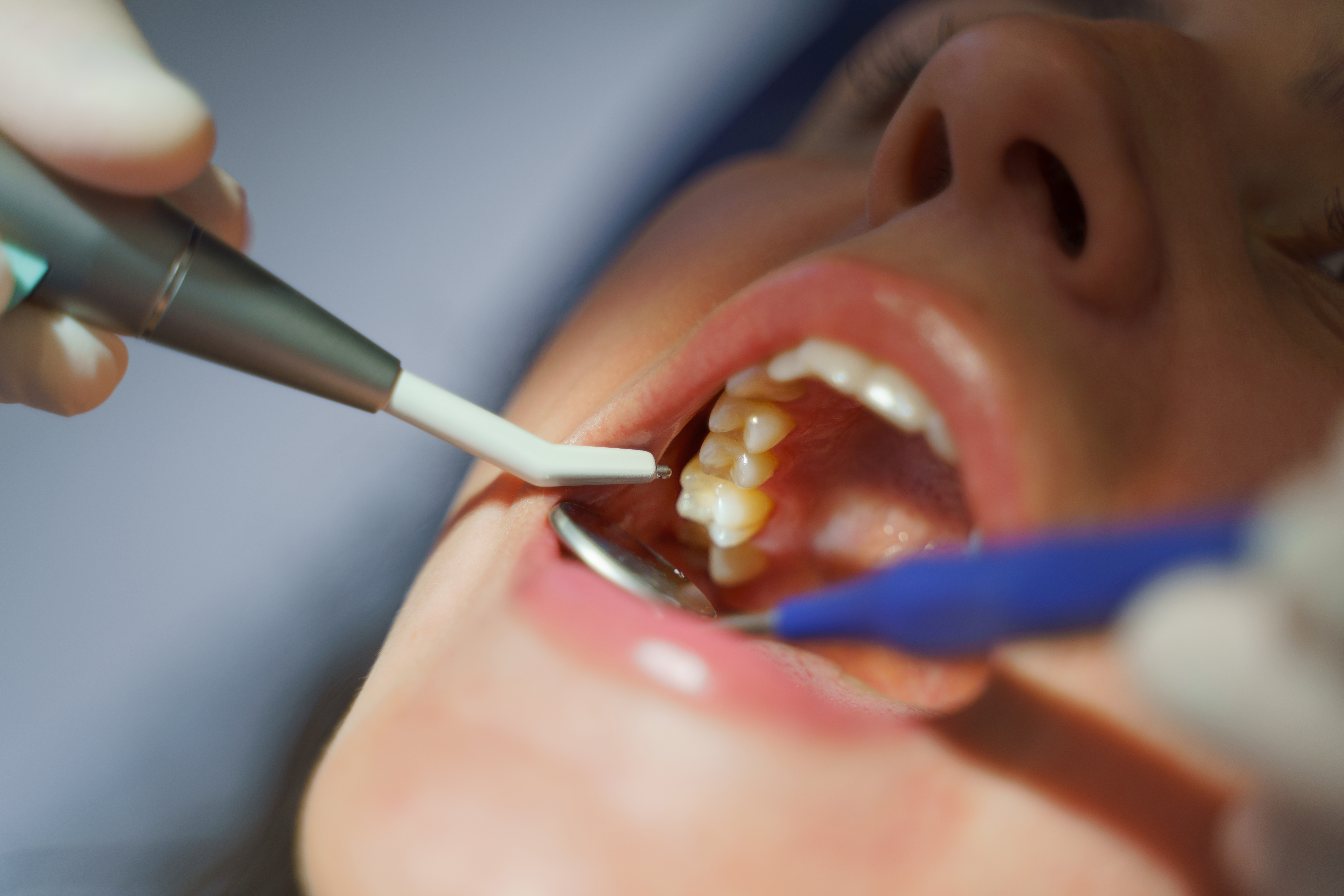
Why Professional Cleanings Are Non-Negotiable
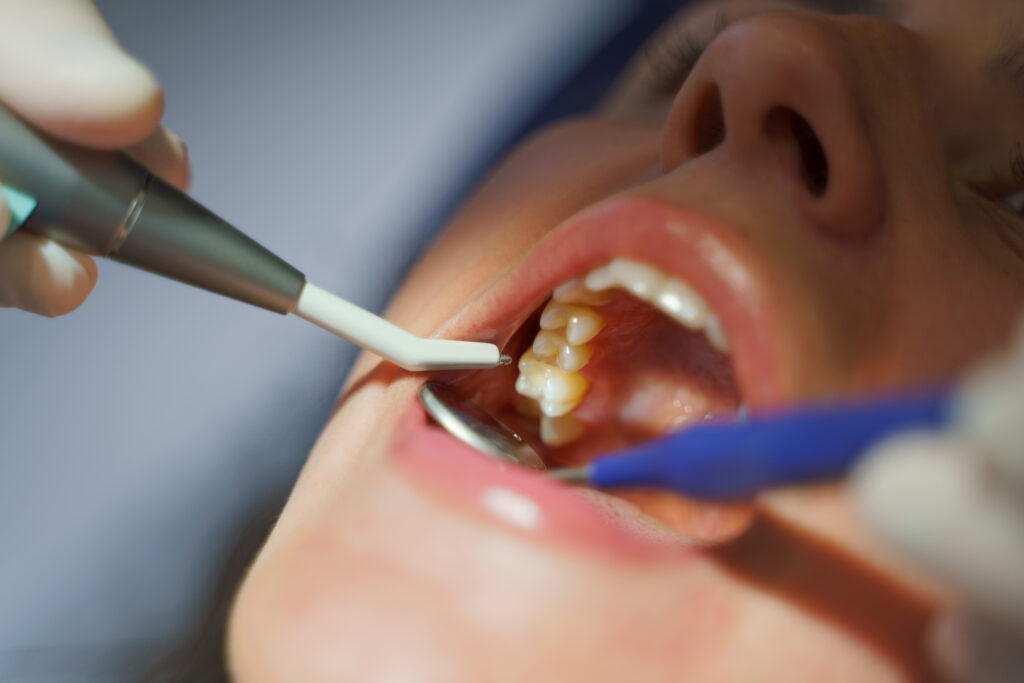
Once tartar forms, the only way to remove it is through a professional cleaning. During the procedure, a skilled dentist or hygienist will use special tools to carefully scrape away tartar from above and below your gumline.
Professional cleanings not only prevent gum disease and cavities but also give your teeth a smoother surface, making it harder for plaque to stick moving forward.
Experience Top-Notch Care at Lane and Associates
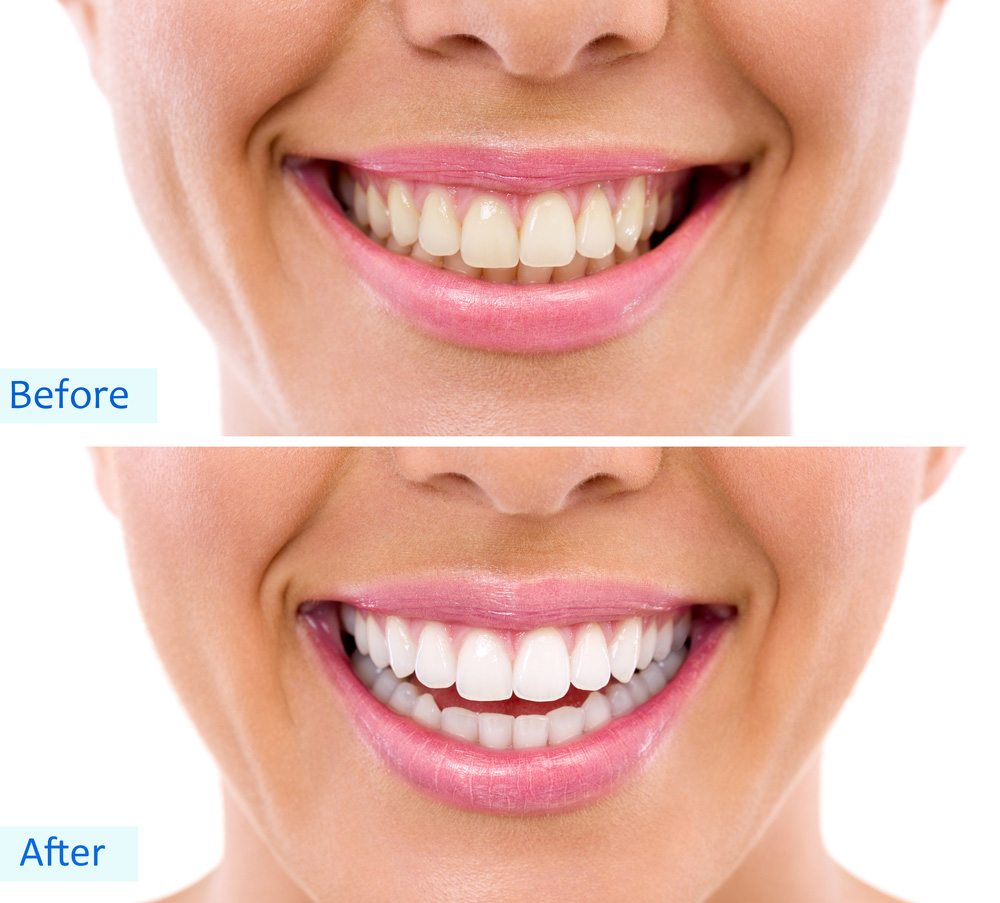
If you’ve noticed signs of tartar buildup, such as discoloration, rough spots, or bleeding gums, it’s time to book a dental appointment. At Lane and Associates Family Dentistry, we specialize in keeping smiles healthy and happy. With over 40 years of experience, our team offers gentle, personalized care for everything from routine cleanings to advanced treatments.
We use the latest techniques to remove tartar effectively and make recommendations to improve your routine at home. With multiple locations across North Carolina, excellent dental care has never been more convenient.
Take Charge of Your Oral Health
While water flossers can’t remove tartar, they shine as a tool for preventing it. Combined with good brushing habits, regular flossing, and professional cleanings, they help pave the way for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Are you overdue for a dental cleaning? Contact Lane and Associates today to schedule your appointment. We’re here to give you the care and guidance you need to keep your teeth and gums in top shape!

Contact Lane and Associates Today For Tartar Removal
Schedule Your Visit
Call us at 1-877-LANE-DDS or visit our website to find the Lane and Associates location nearest you. Your brighter, healthier smile starts here! If you have noticed that plaque has begun to calcify on your teeth, contact Lane and Associates today to schedule a professional dental cleaning and tartar removal. Our experienced dentists will use the latest techniques and tools to remove any calculus buildup and help you maintain good oral health. We have offices located across North Carolina. Don’t wait, call us today!