Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Relief
Persistent head pain that won’t respond to rest or painkillers often has an unexpected source: wisdom teeth. Understanding whether impacted or erupting third molars are triggering your headaches can lead to lasting relief. In this guide, we explain how wisdom teeth cause headaches, classify the types of pain involved, identify key symptoms, explore underlying factors beyond impaction, and outline effective home remedies, professional treatments, and post-extraction care. Lane & Associates Family Dentistry combines advanced imaging, expert oral surgeons, and patient-focused comfort to resolve headaches linked to wisdom tooth issues.
- The connection between wisdom teeth and head pain via pressure and nerve irritation
- Classification of tension, migraine, sinus, and referred-pain headaches
- Recognizing jaw pain, gum swelling, and referral to ear and neck
- Causes beyond impaction such as infection, cysts, bruxism, and TMJ
- Proven home remedies, over-the-counter medications, and extraction benefits
- Post-operative headache management and when to seek expert evaluation
** This is not medical advice, each case is uniquely different consult a trained professional **
Wisdom teeth can cause headaches when pressure from erupting or impacted third molars irritates surrounding structures and nerves. This pressure compresses the jawbone, inflames the gums, and sends referred pain through the trigeminal nerve, manifesting as head pain. For example, an angled wisdom tooth pushing against the jaw nerve can trigger a dull, throbbing ache across the temple region, bridging dental issues to headache relief strategies.

What Is the Role of Impacted Wisdom Teeth in Headache Development?
Impacted wisdom teeth occur when third molars fail to fully erupt, causing them to push against adjacent teeth and bony walls. This impaction creates localized inflammation and nerve compression that translates into headache symptoms. For instance, a horizontally impacted molar pressing on the mandibular nerve can send pain signals up to the forehead and temples, setting the stage for trigeminal irritation.
How Does the Trigeminal Nerve Link Wisdom Teeth to Head Pain?
The trigeminal nerve transmits sensation from the teeth and facial structures to the brain, so irritation of this nerve by an impacted molar can lead to headache. When inflammation or pressure affects the mandibular branch, pain signals travel upward, causing referred pain in the temples, cheeks, or even behind the eyes. Recognizing this nerve pathway clarifies why dental pressure often feels like a migraine.
Can Erupting Wisdom Teeth Exert Pressure That Leads to Headaches?
As wisdom teeth emerge, they exert force on the jawbone and neighboring teeth, creating muscular strain and nerve irritation that can manifest as headaches. This eruptive pressure peaks when the gums become swollen and the bone shifts to accommodate the new tooth. Understanding this eruption process highlights why early evaluation by an oral surgeon at Lane & Associates can prevent chronic head pain.
What Types of Headaches Are Caused by Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth issues can trigger several headache categories, including tension-type pain from jaw muscle fatigue, migraine-style attacks due to nerve sensitization, sinus headaches via upper molar proximity to sinuses, and referred-pain headaches when dental nerves misfire. Recognizing these distinct patterns helps identify the most effective relief strategies.
|
Headache Type
|
Mechanism
|
Typical Symptoms
|
|
Tension Headache
|
Jaw muscle strain from pressure
|
Dull, bilateral “band-like” pain
|
|
Migraine
|
Trigeminal nerve sensitization
|
Throbbing pain, nausea, light sensitivity
|
|
Sinus Headache
|
Sinus cavity pressure from upper molar
|
Facial pressure, nasal congestion, thick mucus
|
|
Referred Pain Headache
|
Nerve cross-signals in jaw and skull
|
Toothache with radiating head or temple pain
|
These classifications guide targeted treatments and clarify why some headaches respond to dental intervention.
How Do Tension Headaches Relate to Wisdom Teeth Issues?
Tension headaches linked to wisdom teeth stem from prolonged jaw muscle contraction as the mouth adjusts to erupting or misaligned molars. Muscle fatigue in the masseter and temporalis manifests as a pressing pain across the forehead and scalp. Alleviating this tension through jaw-relaxation techniques can reduce headache frequency.
Can Wisdom Teeth Trigger Migraines or Sinus Headaches?
Migraines and sinus headaches can originate from wisdom tooth irritation when nerve pathways or sinus membranes become inflamed. Upper molars share nerve roots with sinus cavities, so gum inflammation or impaction can spread, triggering both congestion and migraine pathways via the trigeminal system.
What Is Referred Pain and How Does It Cause Headaches from Wisdom Teeth?
Referred pain occurs when sensory nerves convey tooth pain signals to other head regions, leading to perceived headache. The mandibular and maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve can confuse signals, making pain felt in the temple, cheek, or even behind the eyes. Recognizing referred pain clarifies why tooth troubles often feel like primary headache disorders.
What Are the Symptoms of Wisdom Teeth Headaches? How to Identify Them
Symptoms of wisdom teeth headaches include jaw tenderness, gum swelling, ear or neck pain, and radiating head discomfort that worsens with chewing or mouth opening. These signs differentiate dental headaches from primary neurological conditions and guide appropriate treatment.
Which Jaw Pain and Tenderness Indicate Wisdom Teeth Problems?
Key jaw-related symptoms often accompany wisdom teeth headaches:
-
Sharp or dull aching behind the second molar radiating toward the ear.
-
Tenderness when pressing the rear gum line near the molars.
-
Difficulty fully opening the mouth due to muscle tension.
Persistent jaw pain in these regions signals a dental origin of headache.
How Do Swollen Gums and Pericoronitis Signal Headache Causes?
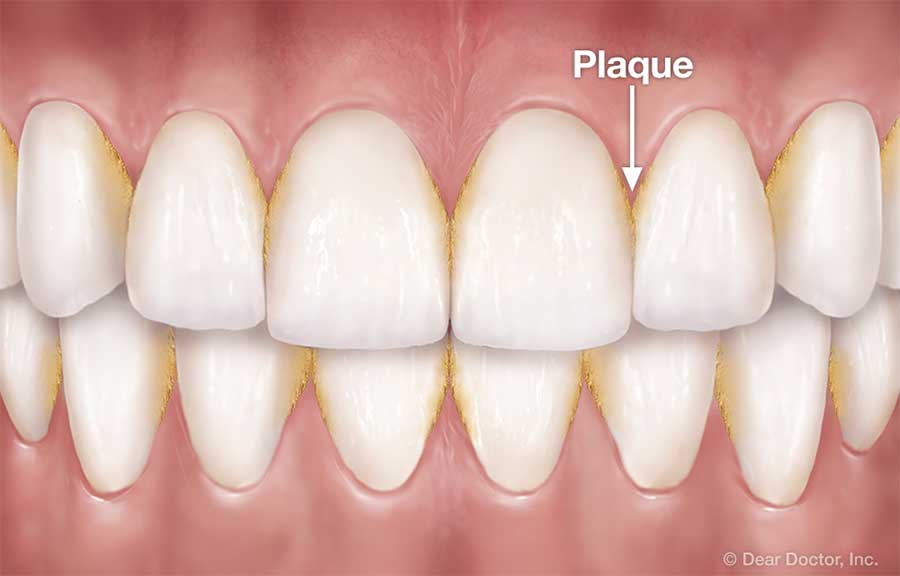
Gum swelling and pericoronitis develop when partially erupted wisdom teeth harbor bacteria, leading to infection and inflammation that can radiate head pain. Pericoronitis inflammation triggers pain receptors in the gingiva, and the resultant systemic inflammatory response often manifests as headache and fever.
Can Wisdom Teeth Headaches Cause Earache and Neck Pain?
Earache and neck pain often accompany wisdom teeth headaches due to nerve overlap and muscular compensation. Inflammation near the jaw can irritate the auriculotemporal nerve branch, producing ear pain and causing neck muscles to tighten in compensation, resulting in tension-related headaches.
What Causes Wisdom Teeth Headaches Beyond Impaction? Infection, Cysts, and TMJ Explained
Beyond impaction, wisdom teeth headaches may arise from pericoronitis, cyst formation, bruxism-induced muscle strain, malocclusion, and TMJ disorders that affect jaw joint health. Addressing these broader causes ensures comprehensive relief.
How Does Pericoronitis Lead to Headaches?
Pericoronitis is an infection of the gum tissue around a partially erupted tooth, causing inflammatory mediators to trigger headache. Pain receptors in the inflamed gingiva send nociceptive signals via facial nerves, resulting in referred pain to the head and temples.
Can Dental Decay and Cysts from Wisdom Teeth Cause Head Pain?
Cavities and cysts around wisdom teeth can create localized pressure and bacterial toxins that irritate nerves, resulting in headaches. A growing cyst may expand before compressing nerve fibers in the jaw, manifesting as persistent head pain that mimics chronic headache disorders.
What Is the Impact of Bruxism and Malocclusion on Wisdom Teeth Headaches?
Bruxism and misaligned bites force wisdom teeth to exert uneven pressure, escalating muscle tension and headache risk. Teeth grinding strains the masseter muscle and temporomandibular joint, which can refer pain across the skull and exacerbate wisdom tooth–related headaches.
How Does TMJ Disorder Relate to Wisdom Teeth and Headaches?
TMJ disorder arises when jaw joint stress from wisdom teeth misalignment or muscle overuse disrupts normal movement, causing headache. Inflammation in the temporomandibular joint refers pain to the temples, ears, and neck, closely mimicking migraine patterns and requiring specialized management.
How Can You Find Relief from Wisdom Teeth Headaches? Treatment and Home Remedies
Effective relief combines home care, over-the-counter medications, and professional treatments to address both symptoms and root causes of wisdom teeth headaches. Implementing these options can restore comfort and prevent recurrence.
What Home Remedies Help Ease Wisdom Teeth Headaches?
Simple home remedies can reduce inflammation and ease pain associated with wisdom teeth headaches. Try these at-home strategies for temporary relief:
-
Apply a warm compress to the jaw to relax muscles and improve circulation.
-
Use a cold pack on the cheek to reduce gum inflammation.
-
Rinse with warm salt water to cleanse bacteria and soothe swollen tissues.
-
Maintain gentle oral hygiene to prevent debris buildup around wisdom teeth.
These measures offer quick symptom control while preparing for professional evaluation.
When Are Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers Effective for Wisdom Teeth Headaches?
Over-the-counter pain relievers provide targeted headache relief when inflammation and muscle strain drive the pain. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen inhibit inflammatory mediators and reduce swelling, while acetaminophen manages discomfort in patients with sensitive stomachs or contraindications.
How Does Wisdom Tooth Extraction Provide Headache Relief?
Surgical removal of problematic wisdom teeth eliminates the source of nerve irritation and pressure, leading to permanent headache resolution. An oral surgeon at Lane & Associates uses gentle techniques and advanced anesthesia to extract teeth safely, restoring comfort and preventing future dental headaches.
What to Expect After Wisdom Teeth Removal: Managing Post-Operative Headaches
Headaches after extraction can occur due to anesthesia effects, jaw stiffness, and healing inflammation, but proper care mitigates these symptoms and supports smooth recovery.
Why Do Headaches Occur After Wisdom Teeth Extraction?
Post-surgical headaches often stem from residual anesthetic effects, muscle tension, and stress on the jaw during the procedure. Jaw immobilization, swelling, and minor sinus cavity shifts can contribute to dull, throbbing head pain in the days following surgery.
How Can Dry Socket Cause Post-Extraction Headaches?
Dry socket develops when the blood clot at the extraction site dislodges, exposing bone and nerve endings that intensify facial and head pain. Severe pain often radiates to the temple and can persist for days without proper intervention.
What Are Effective Ways to Manage Headaches After Surgery?
Recommended strategies for post-extraction headache care:
-
Follow prescribed analgesics and antibiotics exactly as directed.
-
Apply an ice pack intermittently to reduce swelling and headache intensity.
-
Perform light jaw movements to prevent stiffness without dislodging blood clots.
-
Attend follow-up visits to monitor healing and address complications promptly.
These measures ensure both headache relief and optimal recovery.
When Should You See a Dentist or Oral Surgeon for Wisdom Teeth Headaches?
Professional evaluation is necessary when headache symptoms are severe, persistent, or accompanied by signs of infection or jaw dysfunction. Early consultation prevents complications and streamlines treatment. We recommend getting treatment as soon as possible.
What Signs Indicate You Need an Immediate Professional Evaluation for Wisdom Teeth Headaches?
Seek professional care if you experience:
-
Severe, throbbing headache lasting more than 48 hours despite home remedies.
-
Pronounced jaw swelling and redness around a wisdom tooth.
-
Earache combined with high fever or purulent discharge.
-
Restricted mouth opening or unexplained weight loss.
These red flags warrant immediate dental or surgical assessment. If you are experiencing these call a professional now.
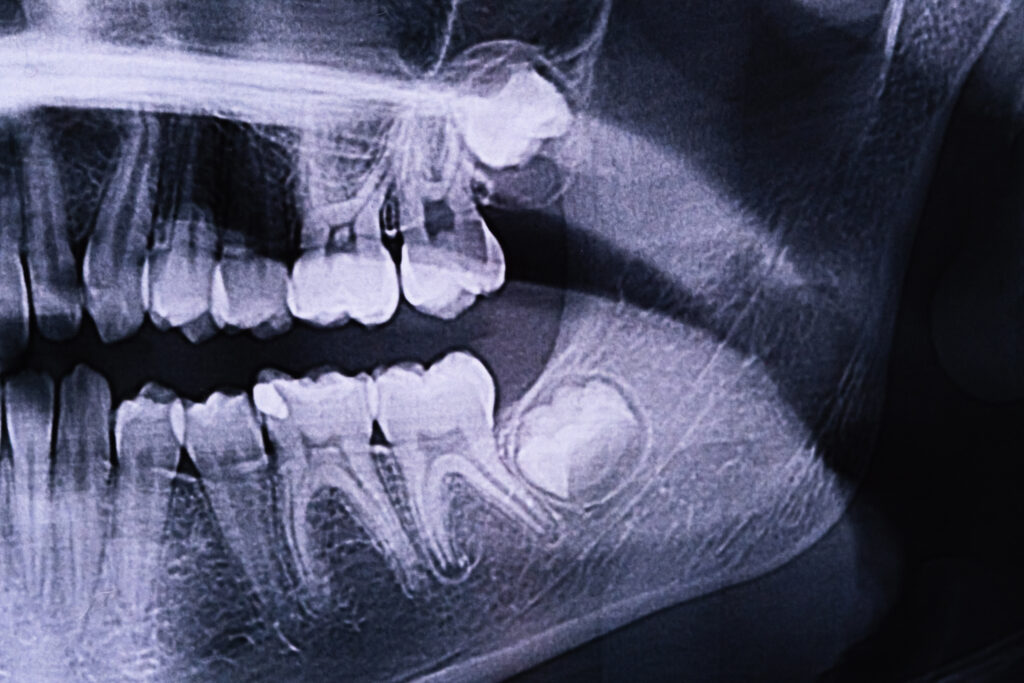
How Are Wisdom Teeth Headaches Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a clinical exam, panoramic X-rays, and sometimes cone-beam CT imaging to assess tooth position, nerve proximity, and bone health. These imaging techniques enable precise treatment planning, whether extraction or conservative management.
Why Is Early Intervention Important for Wisdom Teeth-Related Headaches?
Early intervention prevents complications like chronic headaches, infection, cyst formation, and TMJ damage by addressing problematic wisdom teeth before they worsen. Timely removal or management reduces the risk of extensive surgery, prolonged pain, and misalignment of adjacent teeth.
Persistent headaches linked to wisdom teeth require a clear diagnosis and targeted care to restore comfort and prevent further complications. From identifying impaction and nerve irritation to exploring infection and TMJ influences, understanding these connections empowers informed decisions. Home remedies and OTC options offer temporary relief, while professional extraction often resolves the root cause under expert care. Contact Lane & Associates Family Dentistry for personalized evaluation and lasting relief from wisdom tooth–related headaches.
** This is not medical advice, each case is uniquely different consult a trained professional **